TYPES OF NETWORKS
Based on the size and the coverage area, networks are categorized into the following types:
- Local Area Networks (LANs)
- Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs)
- Wide Area Networks (WANs)
- Personal Area Networks (PANs)
LAN (LOCAL AREA NETWORK)
- A local-area network (LAN) is a computer network that spans a relatively small geographical area like single room, building, office, school , home, hospital etc
- The smallest LAN may only use two computers, while larger LANs can accommodate thousands of computers
- Size is limited to a few kilometers.
- Data transmits at a very fast rate (speed from 10 Mbps to 10 Gbps )
- Its set up involves lower cost as compared to MAN’s and WAN’s. It uses relatively inexpensive hardware (Such as hub/switch, network adapters and Ethernet cables)
- LAN’s can be either wired (twisted pair cables / coaxial cables/ OPTICAL FIBER) or wireless.
- If wired ,the extent of the cable defines the LAN
- A computer is attached to a LAN using a Network Interface Card (NIC), a communications device inside each computer, printer or other machine attached to the network.
- LAN is easy to design and maintain
- privately owned
- Error and noise are the least (since less distance) MOST RELIABLE
- The fault tolerance of a LAN is more, There is less congestion in this network. For example : A bunch of students playing Counter Strike in the same room (without internet).
- Fault tolerance is the property that enables a system to continue operating properly in the event of the failure of (or one or more faults within) some of its components.
MAN (Metropolitan area Network)
- covers a larger area than that of a LAN and smaller area as compared to WAN.
- used to connect various LAN’s (formed by connecting multiple LANs) across several blocks of buildings to entire cities., campus of colleges or universities etc,
- It may serve as an ISP (Internet Service Provider).
- The data transfer rate is moderate , Speeds of MAN ranges in terms of Mbps.
- It’s hard to design and maintain a Metropolitan Area Network.
- The fault tolerance of a MAN is less and also there is more congestion in the network.
- It is costly as compared to LAN.
- MAN is owned and operated by a single entity such as government body or large corporation.
Examples -the part of the telephone company network that can provide a high-speed DSL line to the customer or the cable TV network in a city.
WAN (Wide Area Network)
- spans large geographical area (possibly several continents).
- Speed generally lower than LAN, MAN
- WAN’s data rate is slow about a 10th LAN’s speed, since it involves increased distance and increased number of servers and terminals etc. Speeds of WAN ranges from few kilobits per second (Kbps) to megabits per second (Mbps).
- WAN may transmit data over high-speed phone lines (PSTN) and wireless links such as satellites.
- WAN wiring is often owned by local or long distance telephone companies or cable television operators. Users may connect their home PCs to a WAN with the help of modems and telephone lines.
- WAN is difficult to design and maintain.
- Similar to a MAN, the fault tolerance of a WAN is less and there is more congestion in the network.
- Due to long distance transmission, the noise and error tend to be more in WAN.
- Devices used for transmission of data through WAN are: Optic wires, Microwaves and Satellites.
- may be limited to an enterprise (a corporation or an organization) or accessible to the public.
Most common example of WAN is Internet.
Personal Area Network (PAN)
- A personal area network (PAN) is the interconnection of electronic information technology devices centered on an individual person’s workspace, typically within a range of 10 meters. (such as computers, smartphones, tablets and personal digital assistants.)
- WPAN ( wireless ) devices lend themselves well to adhoc networking. Adhoc networks in which devices connect directly to each other . Technologies – Bluetooth and Infrared.
Conclusion –
There are many advantages of LAN over MAN and WAN, such as LAN’s provide excellent reliability, high data transmission rate, they can easily be managed, and shares peripheral devices too. Local Area Network cannot cover cities or towns and for that Metropolitan Area Network is needed, which can connect city or a group of cities together. Further, for connecting Country or a group of Countries one requires Wide Area Network.
NETWORK ARCHITECTURES
- Client server (also called Tiered- since levels)
- Peer- to – peer
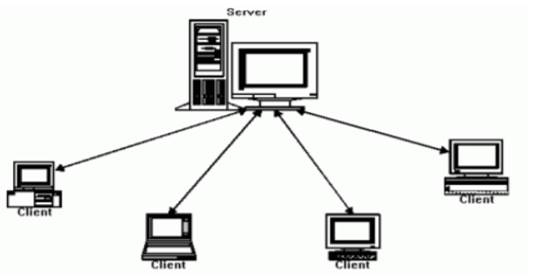
Client server Architecture
Client–server architecture, architecture of a computer network in which many clients (remote processors) request and receive service from a centralized server (host computer).
The server is a high configuration computer (with high processing power and huge storage ), which manages resources of the network and provides services for the other computers on the network.
It has Network OS installed so as to give user access to resources.
e.g. file server, database server, web server, print server
(Both machine and software running on it are referred to as server e.g. web server listens on a port for HTTP requests and send HTTP responses upon receiving requests)

- Routers
- Bridges
- Switches
- Hubs
- Gateway
- Repeaters
Peer- to –peer architecture(network of nodes)
Peer-to-peer (P2P) computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads between peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the application.
Peers make a portion of their resources, such as processing power, disk storage or network bandwidth, directly available to other network participants, without the need for central coordination by servers or stable hosts.[1] Peers are both suppliers and consumers of resources, in contrast to the traditional client-server model in which the consumption and supply of resources is divided. Emerging collaborative P2P systems are going beyond the era of peers doing similar things while sharing resources, and are looking for diverse peers that can bring in unique resources and capabilities to a virtual community thereby empowering it to engage in greater tasks beyond those that can be accomplished by individual peers, yet that are beneficial to all the peers.[2]
While P2P systems had previously been used in many application domains,[3] the architecture was popularized by the file sharing system Napster, originally released in 1999.




